Wireframe Vs Mockup Vs Prototype
Design plays a crucial role in the development process of any digital product or service (like a website and mobile app), regardless of the size of the business. A well-designed product can enhance user experience, boost engagement, and ultimately drive more sales.
Product teams rely on wireframes, mockups, and prototypes to bring their ideas to life and create products that meet the needs of their customers. These terms are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion about their distinct roles in the product development lifecycle.
In this blog post, we aim to clear up any confusion and explore the differences between wireframes, mockups, and prototypes. By understanding the unique role each one plays in the design process, readers will be able to choose the right tool for each stage of website development, ensuring that their products meet the needs of their users and achieve their project goals.
Whether you’re a web designer, developer, or product manager, this article will provide valuable insights into how wireframes, mockups, and prototypes can help you build better products faster. So, let’s dive in and explore these essential tools in the order they appear during the design process.
Contents
Wireframe vs Mockup vs Prototype Difference
Wireframes, prototypes, and mockups are all fundamental design elements used in the development of digital products or services.
- Wireframes are low-fidelity visual representations of a product’s structure and layout.
- Mockups, on the other hand, are high-fidelity representations of a product’s design.
- Prototypes are functional representations of a product that simulate how it will work in the real world.
Wireframes, with basic elements such as content, contrast, icons, and navigation click/tap interactions, are created at the initial stage of the design process to provide a sample version of the future product’s structure.
Mockups, with advanced functionality and polished visual elements, provide a high-fidelity representation of the final product and are used for client presentations or investor pitches.
Prototypes, with additional features such as swipes, scrolls, and digital versions, provide a medium-fidelity representation of the design concept and are used to test out the user experience and interaction design.
Understanding the differences between these design elements can help businesses select the appropriate one for their needs at each stage of the design process. Let’s take a look at each of them:
What is a Wireframe & Why is it Important for Web Design?
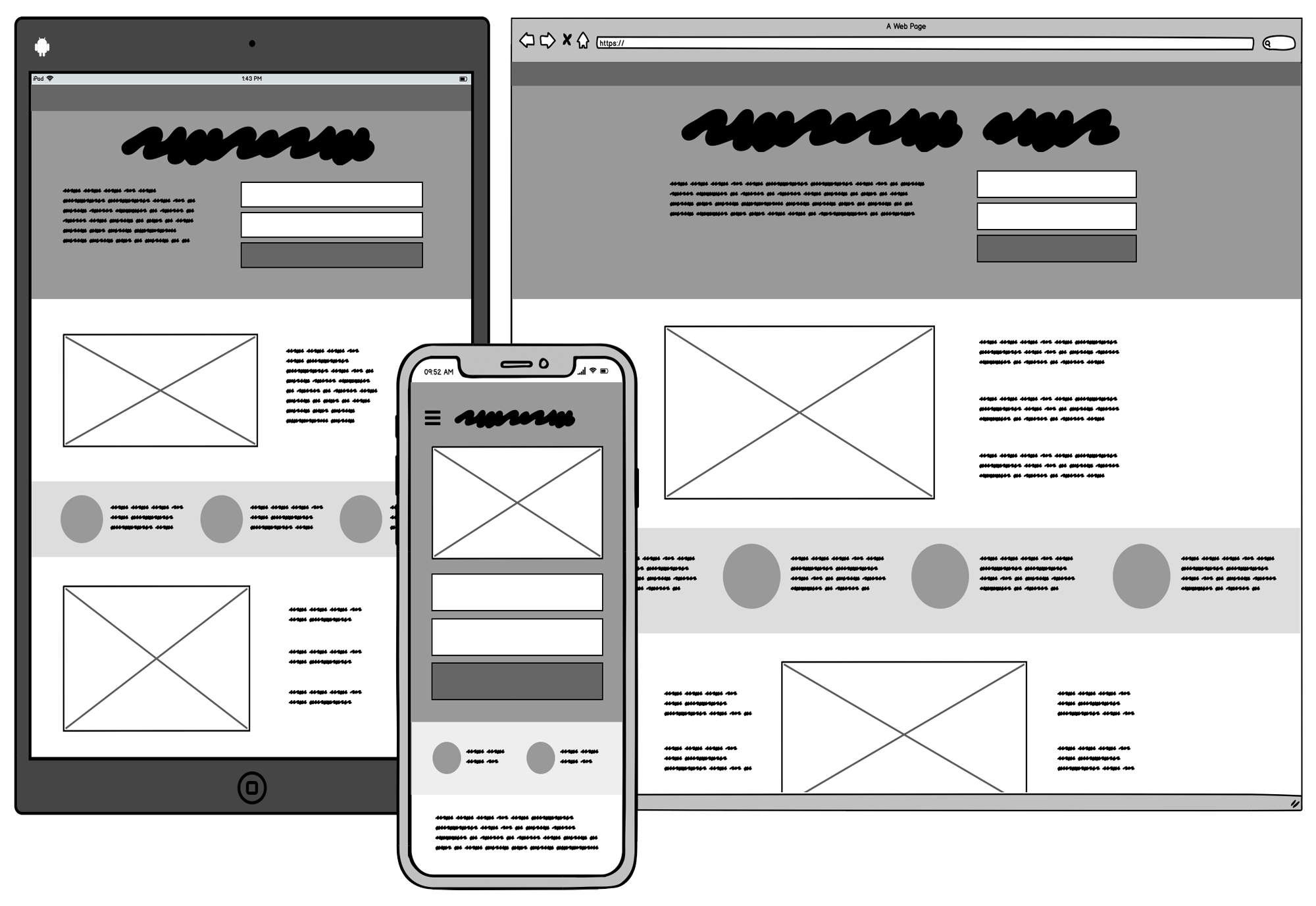
Wireframes are basic, low-fidelity visual representations of a design that outline the structure and layout of a digital product or service. A wireframe creates a blueprint for a digital product, such as a website, web app, or software. They outline each screen with basic lines and shapes, explaining functionality for businesses of all sizes. Designers can create wireframes using pen and paper (paper wireframe) or digital wireframe tools.
Wireframes are basic designs that are used as a foundation for creating a digital product. They are typically black and white and use simple shapes and text to show what the product will look like. They can be created using paper, a whiteboard, or a digital tool. They are used to agreeing on the core features of a product, and feedback should focus on usability rather than visual details like color or logos.
Types of Wireframes
There are several types of wireframes that can be used in the design process, each with varying levels of detail and fidelity. These include:
- Sketch wireframes: These are the simplest type of wireframes, created using a pencil or pen on paper. They are quick and easy to produce and are useful for brainstorming and ideation.
- Digital wireframes: These are wireframes created using digital tools such as Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD. They can be more detailed than sketch wireframes and allow for easier collaboration and sharing with team members.
- Interactive wireframes: These wireframes are designed to simulate user interactions with the product. They may include click/tap interactions, buttons, and links to demonstrate how the product will work.
Examples of wireframes include paper sketches, whiteboard drawings, or digital wireframes created using tools like Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD. Wireframes are an essential part of the design process and help ensure that the final product meets the needs of its users.
Purpose of Wireframes in UX Design
Using a minimalistic structural design to frame your design concept enables quick adjustments and gives an idea of how the future design will look. Wireframe annotations provide an opportunity to share ideas about complex design elements such as colors, shading, or intricate menus.
Wireframes serve several use cases, including:
- Communicating Structure: Wireframes share information architecture about the product’s design, helping stakeholders understand the layout and flow.
- Quick Design: Wireframes provide quick design details, are simple, and are easy to modify, allowing for rapid iteration and feedback.
- Product Discovery: Wireframes aid in identifying business requirements, defining the scope of the product, and exploring potential solutions.
Before committing significant resources to build a UX & UI project, the team must align on what they’re building. Wireframes help ensure everyone understands the goals and objectives of the project before writing any code or allocating resources. Wireframes are a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes in creating successful digital products.
Also, read – The Psychological Impact of UI/UX
What is Prototype & Its Importance in User Interface Design?
After creating a wireframe, the next step in the product design process is to create a prototype, which is a working model of an app or webpage. Prototyping enables designers to test the user journey, identify potential issues with interaction flow, and evaluate how users move between different tasks to achieve desired outcomes.
Types of Prototyping
Prototypes can be low-fidelity or high-fidelity:
- Low-fidelity prototyping: These prototypes are basic and quick to create, providing a rough idea of the design concept. Low-fidelity prototypes can be created using paper and pencil, or simple digital tools such as wireframing software. These prototypes are used to test out the basic layout, structure, and functionality of the design.
- Medium-fidelity prototyping: These prototypes provide a more detailed representation of the design concept, with increased functionality and more refined visual elements. Medium-fidelity prototypes can be created using digital prototyping tools such as InVision, Marvel, or Axure. These prototypes are used to test out the user experience and interaction design of the product.
- High-fidelity prototyping: These prototypes provide a highly detailed and realistic representation of the final product, with advanced functionality and polished visual elements. High-fidelity prototypes can be created using graphic design software such as Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator. These prototypes are used to test out the final look and feel of the product and are often used for client presentations or investor pitches.
Examples of prototypes include clickable website mockups, interactive app designs, physical product models, and even storyboard animations. These prototypes allow designers to test functionality, gather feedback, and refine their product before the final release.
When to Use the Prototype Model?
Prototyping plays a crucial role in the design process by serving multiple purposes, such as:
- Conducting usability tests: Prototypes enable you to put a functional version of your product in the hands of users, allowing you to verify the design’s usability testing before releasing it.
- Validating ideas: Using prototype designs, you can share your ideas at an early stage of the design process, facilitating collaboration with your team to clarify your objectives.
- Facilitating collaborative designs: Prototyping allows you to involve multiple stakeholders, including UX writers, developers, and product managers, in testing the design, and validating navigation, functionality, and user flows.
- Attracting investors and updating stakeholders: In some cases, you may need to create a prototype to demonstrate to stakeholders that your idea has potential and is worth pursuing further.
What is Mockup in Web Design?
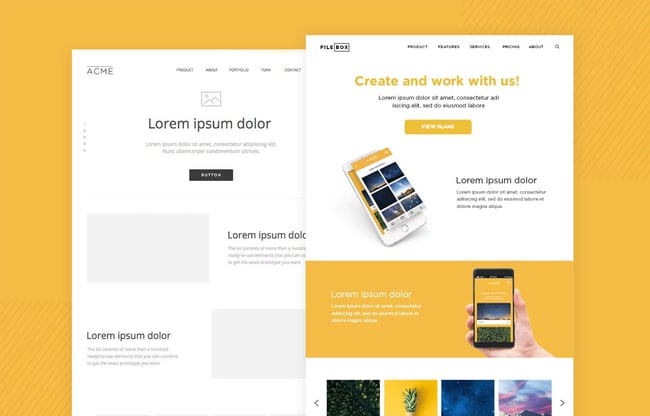
Mockup refers to a preliminary model of a design or product used for demonstration and feedback purposes. A mockup can be a static or interactive representation of the design and helps stakeholders to visualize and evaluate the final product.
Types of Mockups
There are different types of mockups that designers use based on their needs. These include:
- Wireframe Mockup: It is a basic representation of a design, which shows the structure and layout of the product. Wireframe mockups are typically used to create a rough draft of the design and determine its functionality.
- Visual Mockup: This type of mockup includes visual elements such as colors, typography, and images. Visual mockups help to define the visual identity of the product and its brand.
- Functional Mockup: These mockups are interactive and include functional elements such as clickable buttons, dropdowns, and sliders. Functional mockups allow users to experience the product and provide feedback on the user experience.
When To Use a Design Mockup?
Once the concept of mockups is clear, exploring their versatility becomes possible.
- Product discovery: Prior to initiating a project, mockups allow you to experiment with various approaches for your product.
- Ensuring stakeholder alignment: Several individuals contribute to designing and constructing a product, making alignment crucial throughout the process. Mockups can facilitate agreement on the final product and impress potential investors.
- Final design step: The product development cycle relies on designing a mockup, often as part of the design phase.
Irrespective of their usage, mockups function as valuable communication tools, conveying the final product’s appearance. These tools are essential in any designer’s arsenal, as effective communication is always preferable.
Are Prototypes Wireframes and Mockups the Same?
Although the terms “prototype,” “wireframe,” and “mockup” are often used interchangeably, each one serves a different purpose in the product development process. It’s important to understand the differences between these terms to determine which one is suitable for a particular project.
Wireframes, prototypes, and mockups all share the goal of facilitating communication between stakeholders and helping to clarify design decisions. However, they differ in their level of fidelity, functionality, and the purpose they serve in the product development process.
Wireframes communicate a product’s structure from a low-fidelity point of view, mockups highlight a product’s design from a high-fidelity point of view, and prototypes focus on a product’s functionality along with the design. While all three are important in the product design & development process, it’s crucial to choose the right one for a specific project to ensure that the end product meets the desired objectives.
| Category | Wireframe | Prototype | Mockup |
| Purpose | To depict the basic layout and functionality of a design UX project. | To create a functional representation of the design, which can be tested by users. | To provide an impression of the final product’s appearance and user experience. |
| Fidelity | Low-level fidelity | High-level fidelity | High-level fidelity |
| Functionality | No functionality | Lmitied functionality | Full functionality |
| Target Audience | Designers and developers | Designers, developers, and stakeholders | Stakeholders and clients |
| Timeframe | Early stage of design | Mid stage of design | Final stage of design |
| Tools | Pen and paper, digital wireframing tools | Digital prototyping tools | Graphic design software |
| Change | Easy to modify | Modifiable, but with effort | Difficult to modify |
| Cost | Low cost | Medium cost | High cost |
Wireframes, Prototypes, and Mockups Use Cases
When engaging in software product design, it is imperative to gain a comprehensive understanding of the project’s scope, purpose, functionality, and process. Wireframes, mockups, and prototypes are essential components of the design process, with each having its own distinct use cases that can prove advantageous during different stages of the development process.
Wireframes Use Case
Wireframes, in particular, play a crucial role in user experience design, as they enable designers to concentrate on the fundamental elements of a product, including its layout and functionality without getting bogged down in details like color or typography. By using wireframes, designers can quickly recognize potential usability challenges, resulting in significant savings in time and effort in the long run.
For example, when designing an e-commerce website, a wireframe can help designers determine the best placement of essential elements such as product listings, filtering options, and the shopping cart. Wireframes can also help designers to experiment with different user flows and navigation options, ensuring a smooth and intuitive experience for users.
Prototypes Use Case
Prototypes are interactive models of a product that facilitate designers and developers to test and refine its functionality. Developing a prototype identifies the detection and addresses the related issues in the early stages of the development process, reducing the risk of costly UI UX Design Mistakes later on. Prototyping is especially advantageous when creating intricate software products, such as mobile apps or web applications.
For example, suppose you are creating a mobile app for a fitness enterprise. In that case, by designing a prototype, you can assess the user experience of registering and booking a workout session, guaranteeing that the procedure is straightforward and user-friendly. Prototyping also enables the collation of user feedback, streamlining the process of perfecting and enhancing the product before its launch.
Mockups Use Case
Mockups are high-fidelity designs that represent the ultimate product’s appearance in high detail. They are particularly beneficial when communicating with stakeholders, such as investors or clients, as they provide a more genuine representation of the final product. By presenting a mockup, you can assist stakeholders in comprehending how the product will work and how it will fulfill their needs.
For example, if you’re designing a new website for a client. In that case, you can present a mockup to showcase how the website will look, incorporating the color scheme, typography, and layout. This approach will give the client an accurate idea of what to anticipate and make it simpler for them to provide constructive feedback on the design.
The process of design involves a variety of indispensable tools, such as wireframes, prototypes, and mockups, each with its own specific applications.
When employed, these tools can help enhance the quality of products, reduce the expenses associated with development, and streamline communication between stakeholders.
By understanding the unique features of each tool, designers and developers can leverage the most suitable option at each phase of the design process, leading to the achievement of their project goals.
Tools Used For Wireframe vs. Mockup vs. Prototype
Tools used for wireframe, mockup, and prototype creation differ based on the level of detail and functionality required for each stage of the design process.
- Wireframe: In the initial stages of design, designers use low-fidelity wireframes that depict the basic structure and layout of the design. These wireframes can be created using pen and paper or digital wireframing tools such as Adobe XD, Figma, or Sketch.
- Mockup: During the final stages of design, designers create high-fidelity mockups that represent the final look and feel of the design concept. Designers use graphic design software such as Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator to create mockups that showcase the color scheme, typography, and other visual elements of the design.
- Prototype: In the mid-stages of design, designers create interactive prototypes that provide a medium level of detail and limited or no functionality to demonstrate the design concept. Prototypes can be created using digital prototyping tools such as InVision, Figma, Marvel, or Axure.
Each tool serves a specific purpose in the design process and helps designers communicate their design ideas effectively to stakeholders, developers, and clients. By using the appropriate tools for each stage of the design process, designers can ensure that their final product meets the needs and expectations of their target audience.
Wireframes, prototypes, and mockups are essential tools in the design process that help businesses create products that are visually appealing, functional, and user-friendly. These tools are instrumental in effective communication, collaboration, and cost savings, all contributing to a successful product launch and customer satisfaction.
Final Words
Wireframes, prototypes, and mockups each play a unique role in the design process. Wireframes allow designers to create a basic structure and layout of a product, prototypes provide a medium level of detail and limited functionality to demonstrate the design concept, and mockups showcase the final look and feel of the product.
These design tools are crucial for businesses to create products that are visually appealing, functional, and user-friendly. By using the appropriate tool for each stage of the design process, businesses can communicate their design ideas effectively and collaborate with stakeholders, designers, and developers to ensure a successful product launch.
At RedBlink, we specialize in providing top-notch web design services to businesses looking to create exceptional products. Our team of skilled designers uses wireframes, prototypes, and mockups to create products that meet the needs and expectations of our client’s target audience. We are committed to providing a design experience that results in customer satisfaction and loyalty. Contact us today to learn how we can help bring your design ideas to life!
Also please check out our Portfolio to see the exceptional projects we have delivered. Our portfolio showcases our expertise in UI/UX design, wireframes, prototypes, and mockups. By browsing our portfolio, you will get a glimpse of the high-quality solutions we provide to our clients.
Resources –
-
- Prototyping: Paper Versus Digital by Jim Ross
- High-Fidelity or Low-Fidelity, Paper or Computer Choosing Attributes When Testing Web Prototypes by James Landay
- Designing Interactive Systems: People, Activities, Contexts, Technologies by David Benyon
- Measuring the User Experience, Second Edition: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability Metrics
- Designing for the Digital Age – How to Create Human-Centered Products and Services by Kim Goodwin

Director of Digital Marketing | NLP Entity SEO Specialist | Data Scientist | Growth Ninja
With more than 15 years of experience, Loveneet Singh is a seasoned digital marketing director, NLP entity SEO specialist, and data scientist. With a passion for all things Google, WordPress, SEO services, web development, and digital marketing, he brings a wealth of knowledge and expertise to every project. Loveneet’s commitment to creating people-first content that aligns with Google’s guidelines ensures that his articles provide a satisfying experience for readers. Stay updated with his insights and strategies to boost your online presence.
